Free Physics NEET Notes for Atoms And Nuclei
Free Physics Notes for Atoms And Nuclei (NEET)
Power up your NEET Exam prep with Chapter-Wise Physics Notes for Atoms And Nuclei at Onlineneetcoaching.in. Crafted by Brilliant Tutorial experts with 25 years of NEET insights.
- Atoms And Nuclei -
Important Physics Notes for IITJEE/NEET Preparation- Atoms And Nuclei
Class 12 Physics is a broad subject that requires a thorough understanding of the concepts and topics covered. As a result, we have provided Physics Notes PDF for IIT JEE/NEET to students and NEET aspirants. Atoms And Nuclei Class 12 Notes PDF for NEET can be found below. With the help of detailed syllabus, Class 12 students learn what they need to study, how many points are assigned to each unit, and how much time is allotted for each unit. As a result, they can easily plan their study schedule.
Check out the Atoms And Nuclei Class 12 notes PDF for your IIT JEE/NEET Preparation based on the IIT JEE/NEET Physics Syllabus. The Atoms And Nuclei notes PDF is designed in such a way that it is very useful for IIT JEE/NEET aspirants.
Atoms And Nuclei
ATOMS
THOMSON'S ATOMIC MODEL
This model suggests an atom to be a tiny sphere of radius , containing the positive charge. The atom is electrically neutral. It contains an equal negative charge in the form of electrons, which are embedded randomly in this sphere, like seeds in a watermelon.
This model failed to explain
, containing the positive charge. The atom is electrically neutral. It contains an equal negative charge in the form of electrons, which are embedded randomly in this sphere, like seeds in a watermelon.
This model failed to explain
-
large scattering angle of α-particle
-
origin of spectral lines observed in the spectrum of hydrogen atom
ALPHA-PARTICLE SCATTERING AND RUTHERFORD'S NUCLEAR MODEL OF ATOM
In Rutherford α- particle scattering experiment a very fine beam of α-particle passes through a small hole in the lead screen. This well collimated beam is then allowed to fall on a thin gold foil. While passing through the gold foil, α-particles are scattered through different angles. A zinc sulphide screen is placed out the other side of the gold foil, this screen is movable, so as to receive the α-particles, scattered from the gold foil at angles varying from 0 to 180°. When a α-particle strikes the screen, it produces a flash of light.

FINDINGS
-
Most of the α-particles went straight through the gold foil and produced flashes on the screen as if there were nothing inside gold foil. This suggests that the most part of the atom is empty.
-
Few particles collided with the atoms of the foil which have scattered or deflected through considerable large angles. Very few particles even turned back towards source itself.
CONCLUSIONS
-
The entire positive charge and almost whole mass of the atom is concentrated in small centre called a nucleus.
-
The electrons revolving round the nucleus could not deflected the path of α-particles. This suggests that electrons are very light.
In 1911 Rutherford, proposed a new type of model of the atom. According to this model, the positive charge of the atom, instead of being uniformly distributed throughout a sphere of atomic dimension is concentrated in a very small volume at its centre. This central core, called nucleus, is surrounded by clouds of electrons makes the entire atom electrically neutral.
According to Rutherford scattering formula, the number of
α-particles scattered at angle θ by a target,
N ∝ cosec4 (θ/2)
 Impact parameter
Impact parameter
 Distance of closest approach
Distance of closest approach
 RESULT OF RUTHERFORD SCATTERING EXPERIMENT
Nucleus is central, massive, positively charged core, its size of the order of 10–15 m, number of electrons surrounding nucleus is such that atom is electrically neutral.
Unit for nuclear dimension measurement : 1 fermi = 10–15m.
RESULT OF RUTHERFORD SCATTERING EXPERIMENT
Nucleus is central, massive, positively charged core, its size of the order of 10–15 m, number of electrons surrounding nucleus is such that atom is electrically neutral.
Unit for nuclear dimension measurement : 1 fermi = 10–15m.
BOHR’S ATOMIC (HYDROGEN ATOM) MODEL
In 1913 Bohr gave his atomic theory primarily to explain, the spectra of hydrogen and hydrogen-like atoms. His theory, contained a combination of views from Plank’s quantum theory, Einstein’s photon concept and Rutherford model of atom. The Bohr theory can explain, the atomic spectra of hydrogen atom and hydrogen-like ions such as He+, Li2+, Be3+...(one electron ions). But his theory failed to explain, the spectra of more complex atom and ions.
BASIC POSTULATES OF BOHR’S MODEL
-
The electron moves in circular orbits around the nucleus under the influence of coulombic force of attraction between the electron and the positively charged nucleus (as shown in figure below).
 Bohr’s model of hydrogen atom
Bohr’s model of hydrogen atom
-
The electron rotates about the nucleus in certain stationary circular orbits, for which the angular momentum of electron about the nucleus is an integral multiple of
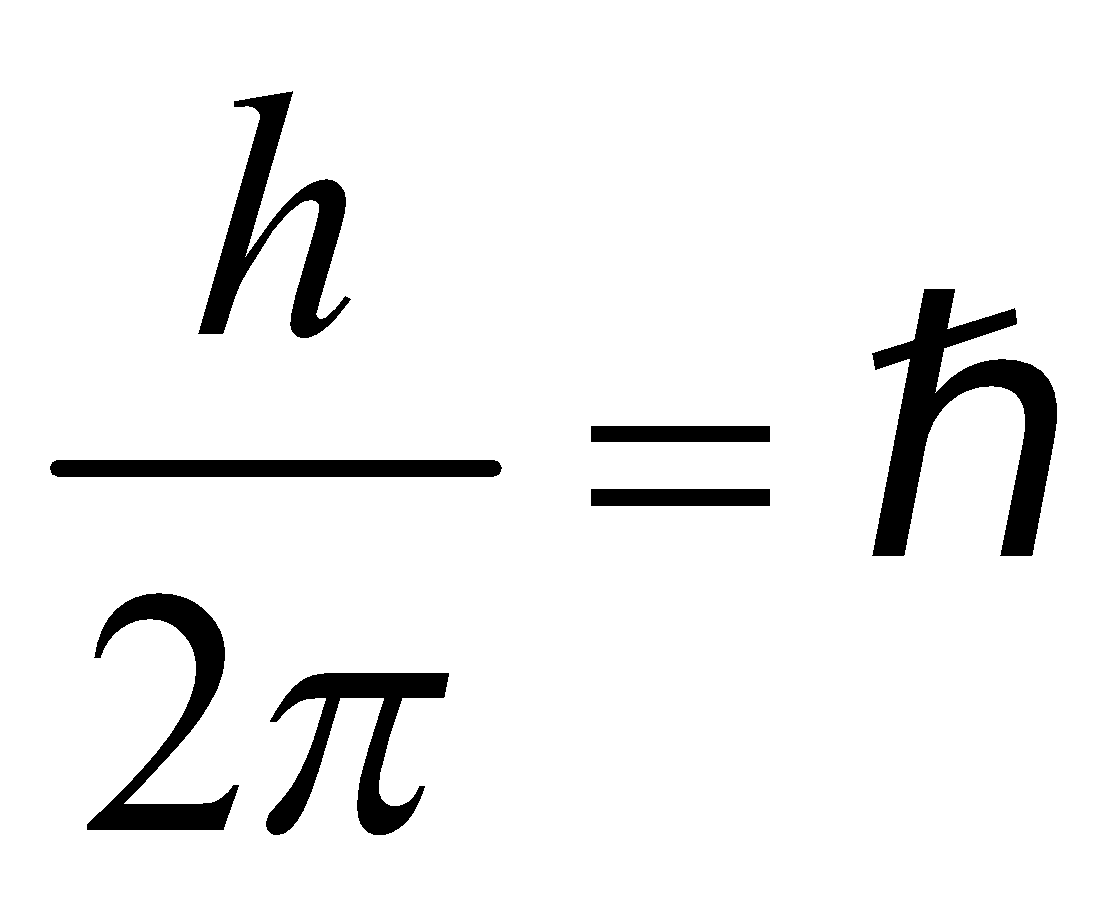 , where h is plank’s constant
, where h is plank’s constant
i.e., Angular Momentum,  ...(1)
(where n = 1, 2, 3......... principal quantum number)
...(1)
(where n = 1, 2, 3......... principal quantum number)
-
When the electron is in one of its stationary orbits, it does not radiate energy, hence the atom is stable. These stationary orbits are called allowed orbits.
-
The atom radiates energy when the electron “jumps” from one allowed stationery state to another. The frequency of radiation follows the condition
hν = Ei – Ef ...(2)
Where Ei and Ef are total energies of initial and final stationary states. This difference in energy (Ei -Ef) between two allowed stationary states is radiated/absorbed in the form of a packet of electromagnetic energy (hν - one photon of frequency ν) called a photon.
Now we calculate the allowed energies of hydrogen atom,
For moving an electron in a circular orbit the required centripetal force is provided by the coulomb force of attraction which acts between nucleus [Ze+, here Z = 1 (atomic number) for hydrogen atom] & electron (e–),
i.e.,  ...(3)
where
...(3)
where  is electrostatic constant & εo is permittivity of free space.
Eliminating v from eqn. (1) and (3) we obtain radius of nth orbit
is electrostatic constant & εo is permittivity of free space.
Eliminating v from eqn. (1) and (3) we obtain radius of nth orbit
 (where n = 1, 2, 3 .....) ...(4)
Equation (4) gives the radii of various orbits (have discrete values).
The smallest radius (also called Bohr radius) corresponds to n = 1 is
(where n = 1, 2, 3 .....) ...(4)
Equation (4) gives the radii of various orbits (have discrete values).
The smallest radius (also called Bohr radius) corresponds to n = 1 is
 ...(5)
⇒ r = 0.529 n2 Å for hydrogen atom and
r = 0.529 ×
...(5)
⇒ r = 0.529 n2 Å for hydrogen atom and
r = 0.529 ×  for hydrogen like ions.
From equation (4) & (1) we obtain,
Velocity of electron in nth state
for hydrogen like ions.
From equation (4) & (1) we obtain,
Velocity of electron in nth state
 or
or 
 (for hydrogen atom ) ...(6)
(for hydrogen atom ) ...(6)
 for hydrogen like ions
for hydrogen like ions
 The total energy of electron is given by
E = K.E. + P.E. = Kinetic energy + Potential energy
The total energy of electron is given by
E = K.E. + P.E. = Kinetic energy + Potential energy

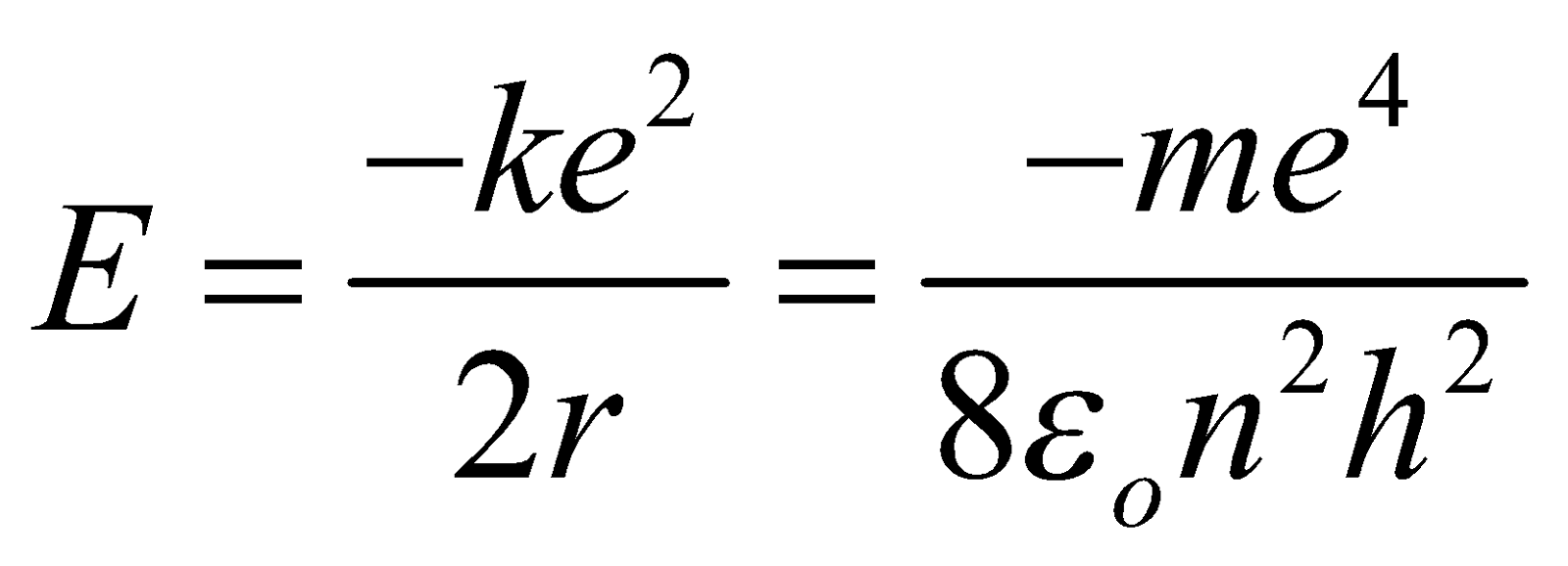 ...(7)
(Allowed energy state)
After substituting numerical values in eqn.(7), we obtain
...(7)
(Allowed energy state)
After substituting numerical values in eqn.(7), we obtain
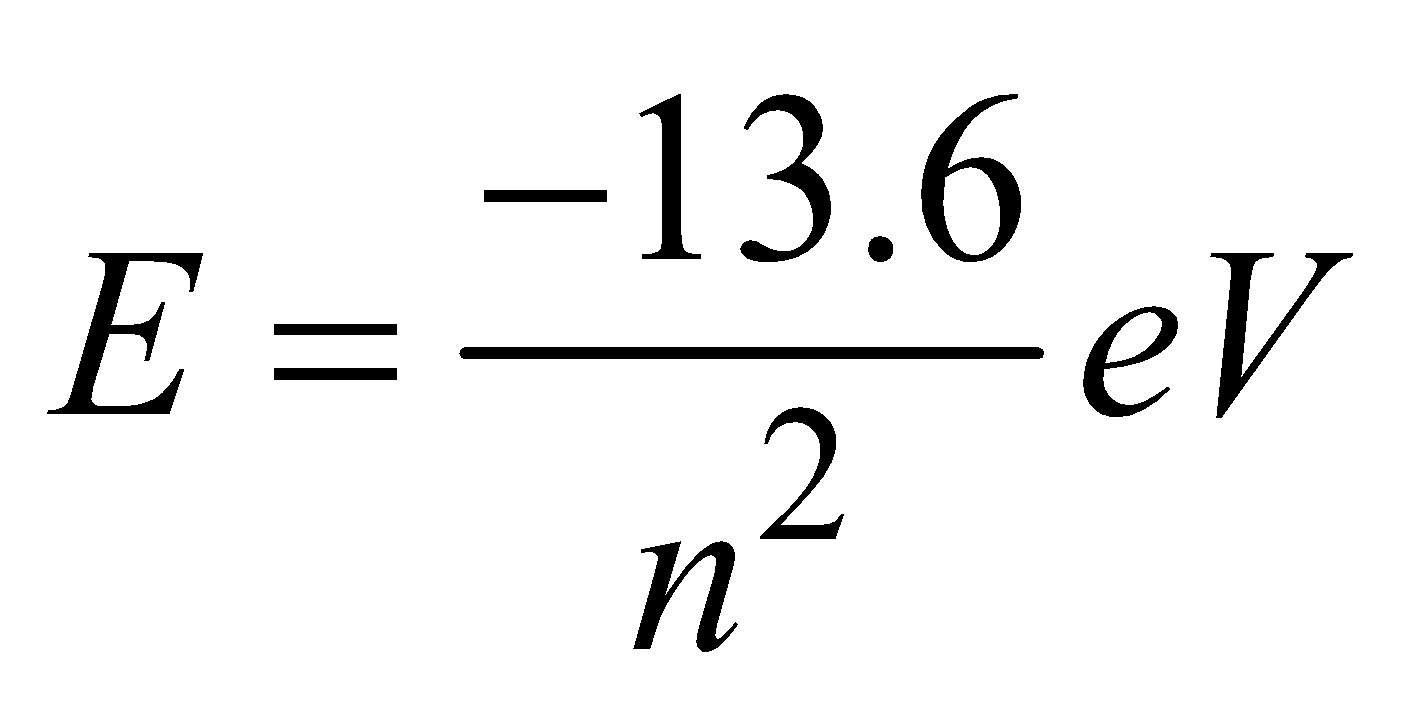 (for hydrogen atom) ...(8)
(for hydrogen atom) ...(8)
 (for hydrogen like ions)
The lowest energy state, or ground state, corresponds to n = 1 is
(for hydrogen like ions)
The lowest energy state, or ground state, corresponds to n = 1 is
 The next state corresponds to n = 2 i.e., first excited state has an energy, E = –3.4 eV
The next state corresponds to n = 2 i.e., first excited state has an energy, E = –3.4 eV
LIMITATIONS OF BOHR'S MODEL
-
It could not explain the spectra of atoms containing more than one electron.
-
There was no theoretical basis for selecting mvr to be an integral multiple of
 .
.
-
It involved the orbit concept which could not be checked experimentally.
-
It could not explain Zeeman & Stark effect and fine lines of spectra.
-
It was against de-Broglie concept and uncertainty principle.
KEEP IN MEMORY
-
Total energy of electron = – Kinetic energy

-
The reference level for potential energy has been taken as infinity
-
The energy gap between two successive levels decreases as the value of n increases
-
The radius difference between the successive orbit (or shells) increases as the value of n increases
-
The velocity of electrons around the nucleus goes on decreasing as n increases
-
The time period of the electron in an orbit

-
Maximum number of spectral lines that can be emitted when an electron jumps from nth orbit is
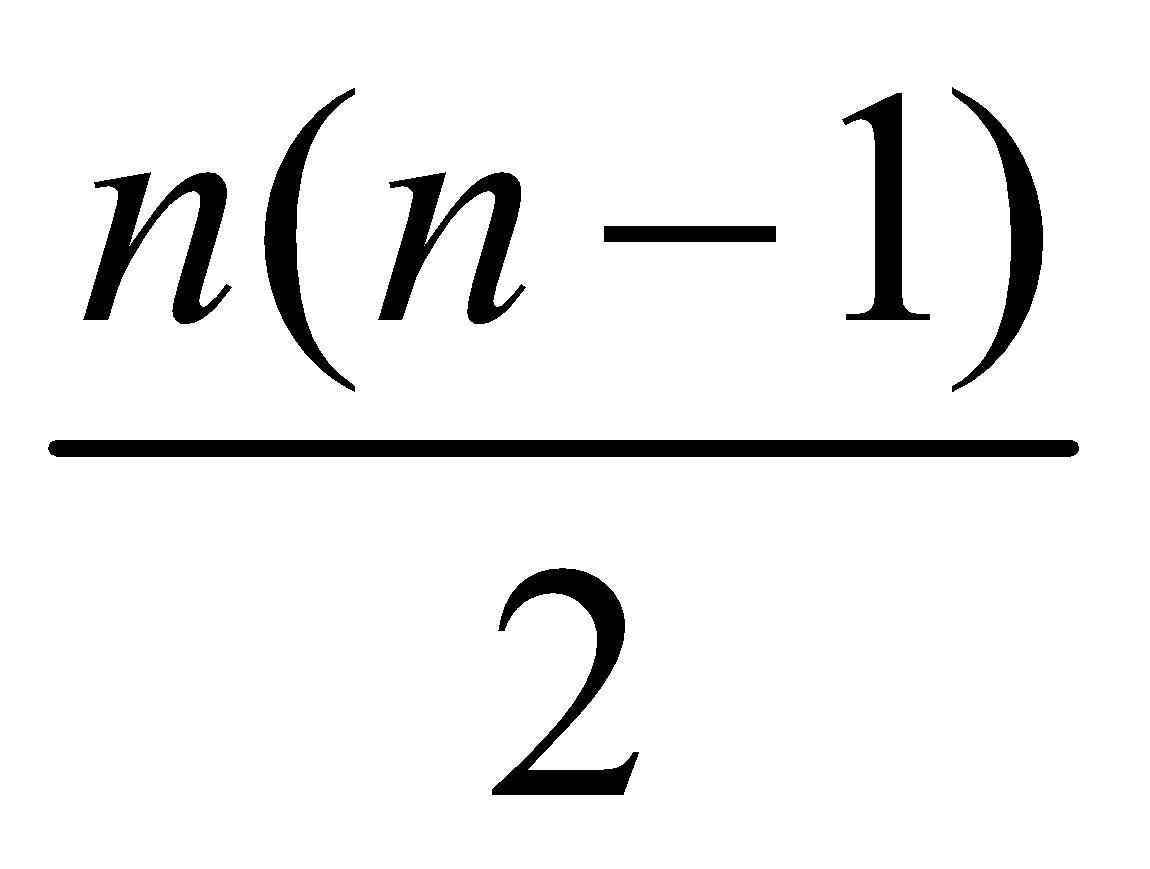
ENERGY LEVELS AND THE LINES SPECTRA OF HYDROGEN ATOM
An energy level diagram of the hydrogen atom is shown in figure. The upper most level corresponding to n→, represents the state for which the electron is completely removed from the atom.
 Some transitions for Lyman, Balmer & Paschen series are shown. The quantum numbers are at left & energies of levels are at right.
E = 0 for r =
Some transitions for Lyman, Balmer & Paschen series are shown. The quantum numbers are at left & energies of levels are at right.
E = 0 for r = (Since n =
(Since n =  )
If the electron jumps from allowed state ni to allowed state nf, then frequency of emitted photon is given by
)
If the electron jumps from allowed state ni to allowed state nf, then frequency of emitted photon is given by
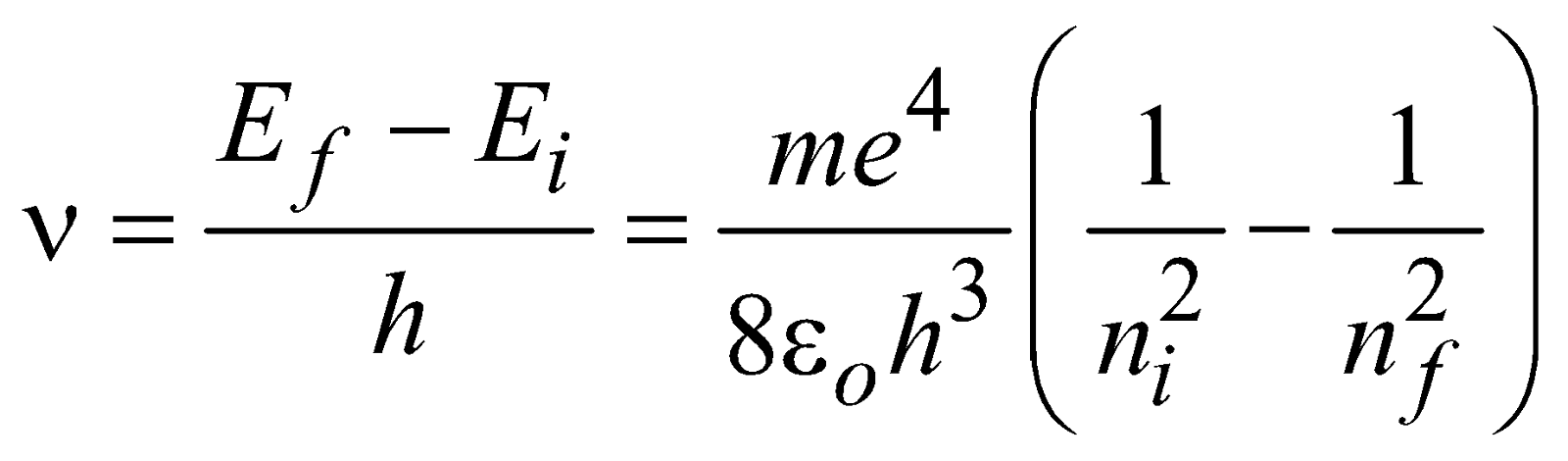 ...(1)
and the wavelength of emitted photon is
...(1)
and the wavelength of emitted photon is
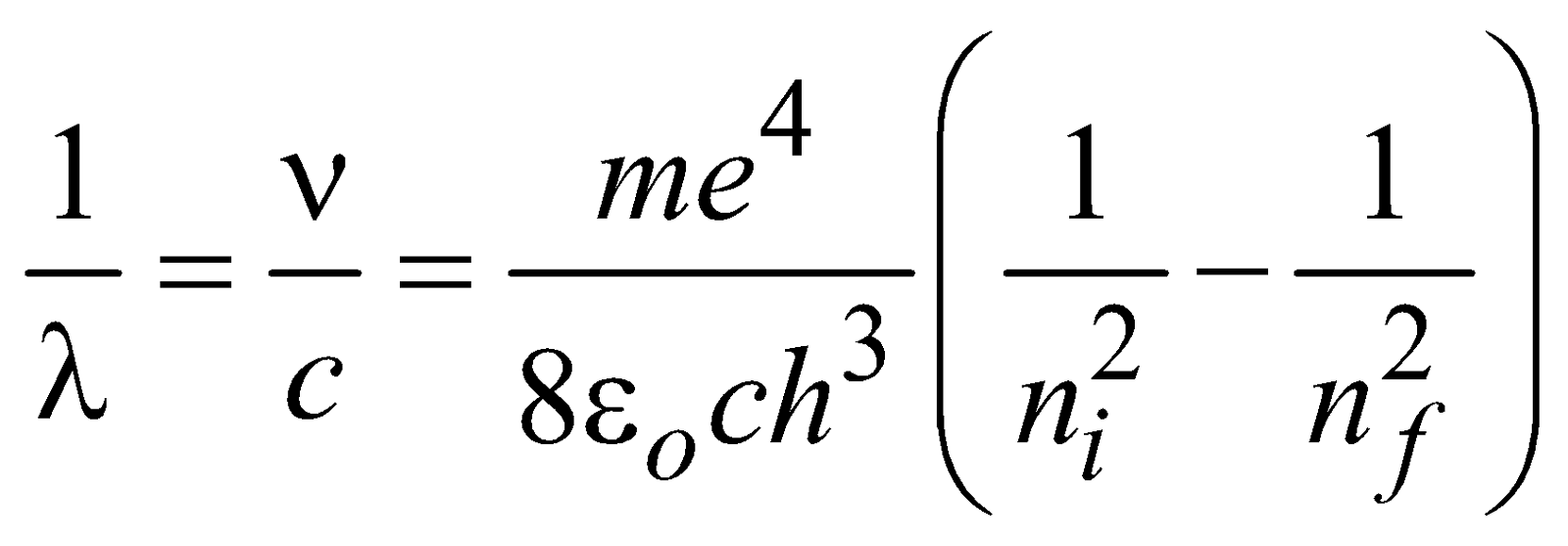
 for hydrogen atom ...(2)
and
for hydrogen atom ...(2)
and  ( for H-like atoms)
where R = 1.096776 × 107m–1 is known as Rydberg constant. By using this expression we can calculate the wavelengths for various series (Lyman, Balmer...) in hydrogen spectrum, i.e.
( for H-like atoms)
where R = 1.096776 × 107m–1 is known as Rydberg constant. By using this expression we can calculate the wavelengths for various series (Lyman, Balmer...) in hydrogen spectrum, i.e.
-
Lyman series ni = 1 & nf = 2, 3, 4...............
-
Balmer series ni = 2, & nf = 3, 4, 5...............
-
Paschen series ni = 3 & nf = 4, 5, 6..............
-
Brackett series ni = 4 & nf = 5, 6, 7...............
-
P fund series ni = 5 & nf = 6, 7, 8...............
First three series of hydrogen atom are shown in figure.
But in practice, the value of Rydberg constant varies between  and R
This is because in above calculations we assumed that electron revolves around a massive fixed nucleus of mass M. But in reality, the electron and nucleus each revolve round their common center of mass i.e., the motion of nucleus cannot be ignored. The correction for nuclear motion amounts to replacing electronic mass m by reduced mass μ which is defined as
and R
This is because in above calculations we assumed that electron revolves around a massive fixed nucleus of mass M. But in reality, the electron and nucleus each revolve round their common center of mass i.e., the motion of nucleus cannot be ignored. The correction for nuclear motion amounts to replacing electronic mass m by reduced mass μ which is defined as
 ...(3)
So total energy by taking this correction is
...(3)
So total energy by taking this correction is
 ...(4)
If we are dealing with hydrogen like ions such as – He+, Li2+, Be3+, Be4+ (one electron ions), each can be considered as a system of two charges, the electron of mass m & charge –e & nucleus of mass M and charge +Ze, where Z is atomic number. The radii of circular orbits for these one electron ions can be written as
...(4)
If we are dealing with hydrogen like ions such as – He+, Li2+, Be3+, Be4+ (one electron ions), each can be considered as a system of two charges, the electron of mass m & charge –e & nucleus of mass M and charge +Ze, where Z is atomic number. The radii of circular orbits for these one electron ions can be written as
 (n = 1, 2, 3............) ...(5)
and the allowed energies are given by
(n = 1, 2, 3............) ...(5)
and the allowed energies are given by
 (n = 1, 2, 3.........) ...(6)
(n = 1, 2, 3.........) ...(6)
WAVELENGTH LIMITS IN VARIOUS SPECTRAL SERIES OF HYDROGEN ATOM
-
For Lyman series (lies in ultraviolet region)
 Here
Here 
-
For Balmer series (lies in visible region)
 Here
Here 
-
For Paschen series (lies in infrared region)
 Here
Here 
-
For Brackett series (lies in infrared region)
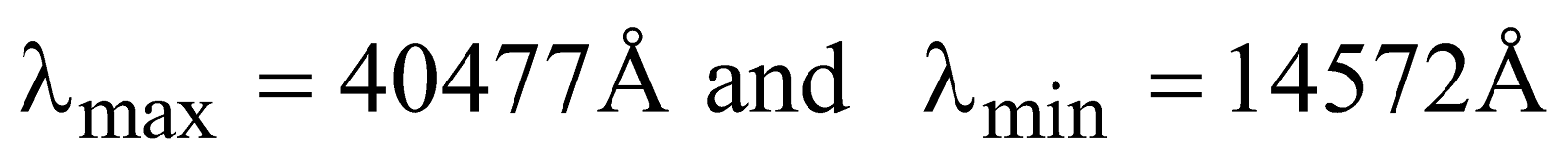 Here
Here 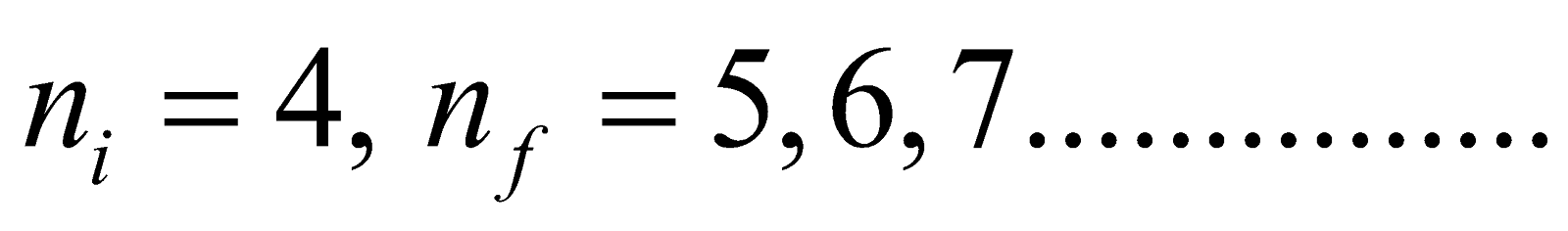
-
For p-fund series (lies in infrared region)

Here 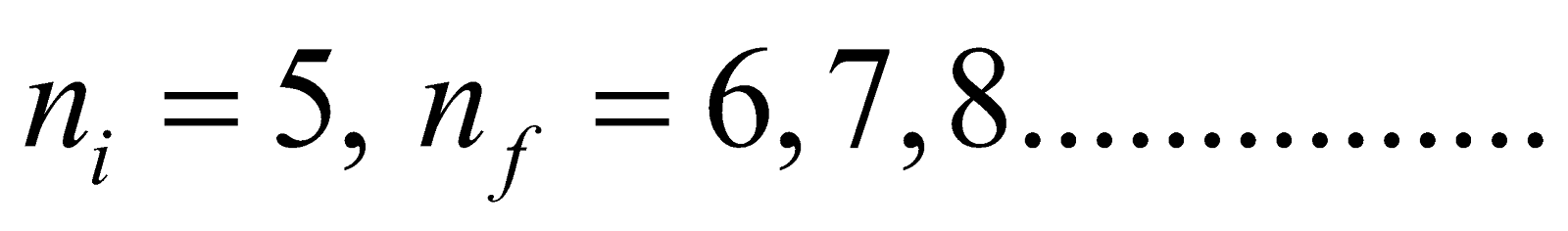
KEEP IN MEMORY
-
The first line of Lyman series is when electron jumps from 2 → 1, It is also called α–line
The second line of lyman series is when electron jumps from 3 → 1, It is also called β–line
The limiting line of lyman series is when electron jumps from ∞ → 1
-
Energy of electrons in different orbits in an atom varies inversely with the square of the number of orbits. So, energy of electrons increases (decreases in negative) as the orbit becomes higher.
-
If energy of a particular orbit is E for H-atom then its value for a H-like atom with atomic number Z is given by E' = E × Z2.
-
If the radius of a particular orbit of H-atom is R then its value for a H-like atom is given by

-
If velocity of an electron in a particular orbit of H-atom be v then its value for H-like atom is given by
v'= v × Z.
-
If kinetic energy and potential energy of an electron in a particular orbit of H-atom be T and V respectively then their corresponding values for H-like atom are given by
T' = T × Z2 and V' = V× Z2.
COMMON DEFAULT
🗶 Incorrect. Bohr's formula for spectral lines does not differentiate between isotopes. For example the first line of Lyman series in hydrogen and deuterium will have same wavelength because

✔ Correct. The value of R will be different for hydrogen and deuterium and therefore λ will be different for the two cases. In fact

α-particles scattered at angle θ by a target,
Here
T' = T × Z2 and V' = V× Z2.
NUCLEI
SOME IMPORTANT FACTS ABOUT ATOMIC MASS, SIZE AND COMPOSITION OF NUCLEUS
- Proton was discovered by Goldstein
- Atomic mass unit
1.a.m.u = 1/12th of mass of C-12 isotope,
1 a.m.u = 1.660565 × 10–27 kg - Mass of a proton, mp = 1.0073 a.m.u = 1.6726 × 10–27 kg
- Chadwick’s experiment
Neutrons were detected. - Mass of neutron, mn = 1.00866 a.m.u = 1.6749 × 10–27 kg
- Mass of electron = 9.1 ×10–31 kg
- Mass number, A = total number of nucleons (neutrons + protons present in the nucleus of an atom)
- Atomic number, Z = number of protons = number of electrons
- Types of nuclei :
- Isotopes : The atoms of the element which have the same atomic number but different atomic mass numbers. e.g., 1H1, 1H2, 1H3 ; 8O16, 8O17, 8O18
- Isobars : The atoms of differents element which have the same atomic mass number but different atomic numbers. e.g., 6C14, 7N14, 18Ar40, 20Ca40 etc.
- Isotones : The nuclides which contain the same number of neutrons e.g., 2H23, 2He24, 2Be59, 5Be510 etc.
- Isomers : having same mass number, same atomic number but different radioactive properties.
- Rest mass of nucleus is less than sum of rest masses of constituent nucleons, the difference is called mass defect.
- Size of the nucleus : Radius of nucleus, R = R0 A1/ 3 where R0 = 1.1 × 10–15 m.
- Nuclear density of all elements ~ 1017 kg m–3.
MASS ENERGY AND NUCLEAR BINDING ENERGY
BINDING ENERGY
- A nuclide is a specific nucleus of an atom characterised as ZXA where A = mass number and Z = atomic number.
- Binding energy per nucleon is nearly 8.4 MeV for nuclei in the range of mass number 40 to 120.
- Binding energy is highest in Fe56.( 8.8 MeV)
- Binding energy curve predicts :
- Fission : Breaking up of a heavy nucleus (A > 200) into two nuclei of approximately equal size, and release of energy.
- Fusion : Lighter nuclei ( A < 20) combine together to form heavier nucleus and release of energy.
- BE/ A varies by less than 10% above A = 10 suggests that each nucleon interacts with its neighbouring nucleon only.
- For A > 56, BE/A decreases because of the destabilising effect of long-range coulombic force.
NUCLEAR FORCE
CHARACTERISTICS OF NUCLEAR FORCE
- It is a short range force effective only in range 10–15 m
- It is charge independent. It acts between proton-proton, proton-neutron and neutron – neutron.
- It is not a central force.
- It is spin dependent.
- It is 1038 times stronger than gravitational force and 102 times stronger than electric force.
- The main cause of nuclear force is the exchange of π− mesons between nucleus
RADIOACTIVITY
- α-rays (i.e., Helium nuclei or α – particles)
- β-rays (i.e., electron or positron or β – particles)
- γ-rays (photons or gamma radiations)
- chemical combination
- changing physical environment other than nuclear bombardment
FEATURES OF RADIOACTIVITY
- It is a statistical process.
- When a nucleus undergoes alpha or beta decay, its atomic number and mass number changes (in β-decay only atomic number changes) & it transforms into a new element.
(α-particle), it means that by emission of alpha particle (α-particle), it loses 2 units of charge and 4 units of mass.
(positron). It means that by emission of beta particle (β+-particle), nucleus loses one unit of charge. It is surprising to note that a nucleus does not contain β+ then how is it emitted. Reason : During a β+ particle(i.e., positron) decay, a protron converts into a neutron
- When a nucleus emits a gamma ray, neither the mass nor the charge of the nucleus changes
PROPERTIES OF α, β & γ-RAYS
- It is a positively charged particle & contains a charge of 3.2 × 10–19 coulomb (exactly double the charge of electron).
- The mass of α-particles is 6.645 × 10–27kg (It is equal to mass of a helium nucleus). Actually α-particle is nucleus of helium, hence it is called doubly ionised helium.
- They (α-particles) get deflected in both electric & magnetic fields.
- The velocity of α-particle is very less than the velocity of light i.e.,
, where c is velocity of light.
- The range of α-particle in air depends on radioactive substance.
- The ionisation power of α-particle is higher than both β (100 times of β & 10,000 times of γ) and γ particle.
- The penetrating power of α particle is lowest (in comparison to β & γ particles). It is 1/100 times of β-particles & 1/10,000 times of γ-rays.
- The α-particles can produce fluorescence in barium platinocyanide and zinc sulphide.
- They show little effect on photographic plate.
- They show heating effect on stopping.
- The beta particles (i.e., β– or β+) may be positive & negative particle & contain
of charge. Actually β– is electron & β+ is positron.
- They get deflected in both electric & magnetic field.
- The velocity of β-particle varies between 0.01c to .99c, where c is velocity of light.
- The mass of β particle is relativistic, because its velocity is comparable to velocity of light
- They have both ionisation & penetration power. Ionisation power less than α-particle and penetration power more than α-particle.
- They produce fluorescence on barium platinocyanide & zinc sulphide.
- They are electromagnetic waves as x-rays.
- They are not deflected in electric & magnetic field, it means that they are chargeless.
- The velocity of γ-particle is equal to velocity of light.
- The ionisation power of gamma rays is less than β & α rays but penetration power more than β and α-rays.
- The γ-particles are emitted from the nucleus, while X-rays are obtained, when electron goes from one state to another in an atom.
- When γ-rays photon strikes nucleus in a substance, then it gives rise to a phenomenon of pair production i.e.,
RUTHERFORD AND SODDY LAW FOR RADIOACTIVE DECAY
HALF-LIFE OF A RADIOACTIVE SUBSTANCE
MEAN LIFE OF A RADIOACTIVE SUBSTANCE
RADIOACTIVE SERIES
RADIOACTIVE EQUILIBRIUM
CARBON DATING
- Specific activity is the activity of 1 gram of material.
- Geiger Muller Counter is used for detecting α and β particles.
- Cloud chamber is used for detecting radioactive radiations and for determining their paths, range and energy.
- Baryon number
B = 1, for a neutron and a proton. - Lepton number (L)
L = 1 for electron, and neutrino
- Radioactive isotope
- Iodine-131 For detecting the activity of thyroid gland
- Chromium-51 To locate the exact position of haemorrhage
- Phosphorus-32 In agriculture
- C–14 Carbon dating, Photosynthesis in plants
- Co60 Cancer treatment
- Na24 For circulation of blood
NUCLEAR REACTION
- Charge conservation
- Conservation of linear momentum
- Conservation of angular momentum
- Conservation of energy (Rest mass energy + K.E.)
NUCLEAR FISSION (BY OTTO HAHN AND STRASSMANN)
- Nuclear fuel : U233, U235, Pu239 etc.
- Moderator : Graphite, heavy water (D2O). To slow down the neutrons (or slow down the nuclear reaction).
- Control rods : (Cadmium, boron). To absorb excess neutrons. It controls the chain reaction.
- Coolant : (water etc). To remove the heat produced in the core to heat exchanger for production of electricity.
